There exist approximately 320 distinct types of honey, exhibiting variations in color, scent, and taste. Honey predominantly consists of sugar, alongside a combination of amino acids, vitamins, minerals, iron, zinc, and antioxidants. Apart from being a natural sweetener, honey serves as an anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial substance. It is commonly consumed orally to alleviate coughs and applied topically to treat burns and facilitate the healing of wounds.
The Effect of Honey on Cardiovascular Diseases

Honey contains a variety of antioxidants, such as flavonoids and polyphenols, that aid in the reduction of oxidative stress within the body. Oxidative stress has been linked to the development of cardiovascular diseases. Several studies propose that honey has the potential to lower blood pressure, a significant risk factor for heart disease and stroke. This effect may be attributed to the presence of antioxidants and phytonutrients in honey. Additionally, the consumption of honey has been associated with favorable changes in cholesterol profiles. It has the ability to elevate levels of “good” HDL cholesterol while decreasing levels of “bad” LDL cholesterol and triglycerides in certain individuals.
The development of cardiovascular diseases is influenced by chronic inflammation. Honey’s anti-inflammatory properties may aid in reducing the risk of these conditions. The endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels, plays a crucial role in maintaining vascular health. Some studies suggest that honey may enhance endothelial function, which can have a positive impact on cardiovascular health. Excessive body weight is a risk factor for heart disease. By substituting honey for sugar in your diet, you may be able to manage your weight more effectively, as honey is slightly lower in calories and may have a more favorable effect on blood sugar levels. Honey contains a natural substance known as fibrinolytic enzyme, which may help prevent the formation of blood clots, thereby reducing the risk of conditions such as deep vein thrombosis and stroke.
The Effect of Honey of Gastrointestinal Diseases

Honey possesses natural properties that have anti-inflammatory and soothing effects, making it beneficial in relieving irritation and discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract. Scientific evidence suggests that honey may be effective in alleviating gastrointestinal conditions such as diarrhea caused by inflammation of the stomach, known as gastroenteritis. Additionally, honey has the potential to provide relief for conditions like gastritis or acid reflux. Moreover, honey can be a valuable component of oral rehydration therapy. The antibacterial compounds found in honey can help combat harmful bacteria in the digestive system, making it beneficial for conditions involving bacterial overgrowth or infections. Throughout history, honey has been utilized for its wound-healing properties, promoting the healing process of ulcers and other gastrointestinal lesions. Furthermore, honey is commonly used to soothe a sore throat and alleviate coughing, which can be symptoms of certain gastrointestinal conditions or side effects of medications used to treat them. The different types of sugars present in honey can serve as a food source for beneficial gut bacteria, contributing to a healthy balance of gut flora. This prebiotic effect is crucial for maintaining overall digestive health. Lastly, honey contains small amounts of vitamins, minerals, and amino acids, which can contribute to overall nutrition when consumed in moderation.
The Effect of Honey on Neurological Diseases
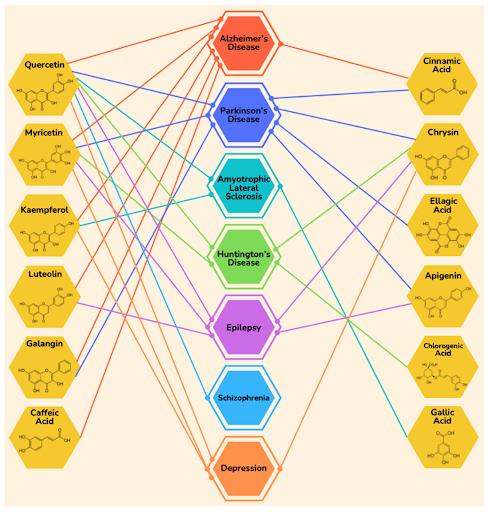
Oxidative stress plays a role in the advancement of neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Honey has the ability to safeguard cells against this stress. Research indicates that honey may have antidepressant, anticonvulsant, and anti-anxiety effects. Some studies have demonstrated that honey can help prevent memory disorders. Chronic inflammation is linked to various neurological conditions, but honey possesses anti-inflammatory properties that can potentially reduce inflammation in the brain and nervous system. Furthermore, adequate sleep is vital for brain health, and honey can contribute to better sleep by increasing serotonin levels, a neurotransmitter that regulates sleep patterns, and by providing a source of glucose to the brain during the night. Certain studies suggest that honey may positively impact cognitive function, enhancing memory and concentration. This can be particularly advantageous for individuals with neurological diseases that impair cognitive abilities. In cases where neurological disorders result in impaired mobility or sensory issues, topical application of honey can aid in wound healing. Its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties can assist in the prevention and treatment of skin sores or pressure ulcers. The glucose and fructose present in honey offer a rapid source of energy to the brain, which can be beneficial for individuals experiencing fatigue or weakness due to neurological conditions.
The Effect of Honey on Cough

EHoney has natural properties that make it an effective cough suppressant. By reducing the frequency and severity of coughing, it enables individuals to find relief and achieve a restful sleep. Its thick consistency aids in lubricating the throat, alleviating the dry and scratchy sensation commonly associated with coughing. Additionally, honey’s natural antibacterial properties help combat bacterial infections that may contribute to the cough. Furthermore, the presence of antioxidants in honey assists in reducing inflammation in the throat and promoting healing. Moreover, honey contains a variety of vitamins, minerals, and enzymes that support the immune system and aid in fighting off infections that may be causing the cough. Research indicates that eucalyptus honey, citrus honey, and labiatae honey can serve as effective cough suppressants for individuals with upper respiratory infections and acute nighttime cough.
The Effect of Honey on Wounds
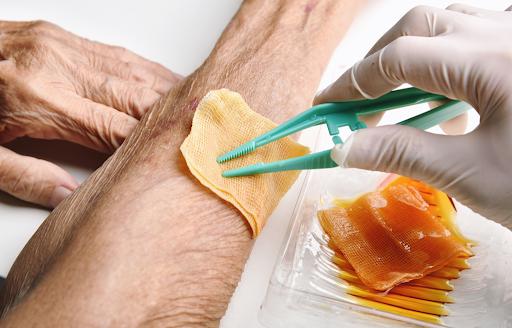
Medical-grade honey has been proven to be effective in promoting wound healing, especially in the case of burns. Its antibacterial properties help prevent infections by creating an environment that is unfavorable for harmful bacteria to grow. The presence of hydrogen peroxide and low water content in honey further contributes to its ability to inhibit bacterial growth. Moreover, honey has anti-inflammatory properties that aid in reducing inflammation in wounds, which is crucial for the healing process. It also helps alleviate pain and swelling around the wound. Additionally, honey stimulates the growth of new tissue and promotes cell proliferation, which accelerates the healing process and leads to more efficient wound healing.
One of the key benefits of honey in wound healing is its ability to maintain a moist wound environment, which is optimal for the healing process. By preventing the wound from drying out, honey promotes the formation of granulation tissue. Furthermore, honey’s anti-inflammatory and tissue regeneration properties may contribute to reduced scarring in the long term, as it supports the formation of healthier tissue. Honey also aids in the debridement of wounds, facilitating the removal of dead or damaged tissue by loosening and dissolving necrotic tissue. Additionally, honey can help minimize unpleasant odors that may arise from infected wounds. Its natural analgesic properties provide pain relief during the healing process for individuals with wounds or burns. The convenience of applying honey to wounds is another advantage, as it can be directly spread onto the wound or used as part of a dressing!
MediHoney

MediHoney offers numerous benefits as it is made with 100% leptospermum honey dressing specifically designed for acute and chronic wounds. It helps maintain a low pH level of 3.5 to 4.5 within the wound environment, promoting optimal healing conditions. Additionally, it is non-toxic, natural, and safe to use. It can be safely applied to tunneled wounds or wounds with undermining, and it remains effective even in the presence of wound fluid, blood, and tissue.
Who should utilize this product?
Individuals with moderate to heavy exudate or those who require light packing for wound care should consider using MediHoney. This includes individuals with conditions such as diabetic foot ulcers, leg ulcers, pressure ulcers, first and second degree partial thickness burns, donor sites, traumatic or surgical wounds, and more.
Safety and Side Effects of Honey

Honey is generally considered to be a safe option when used as a natural sweetener, cough suppressant, or topical treatment for minor sores and wounds. However, it is important to note that honey should not be given to babies under the age of 1 year, even in small amounts. This is because honey can potentially lead to a rare but serious gastrointestinal condition known as infant botulism, which is caused by exposure to Clostridium botulinum spores. These spores can grow and multiply in a baby’s intestines, producing a dangerous toxin.
It is also worth mentioning that some individuals may have sensitivities or allergies to specific components found in honey, particularly bee pollen. While such allergies are rare, they can result in severe and occasionally fatal adverse reactions. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include wheezing, asthmatic symptoms, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, weakness, excessive perspiration, fainting, irregular heart rhythms, stinging after topical application, and potential effects on blood sugar levels.

